
Climate-Friendly Cooking Practices Leading to Conservation of Raptors, particularly Forest Owlet
Climate-Friendly Cooking Practices Leading to Conservation of Raptors, particularly Forest Owlet
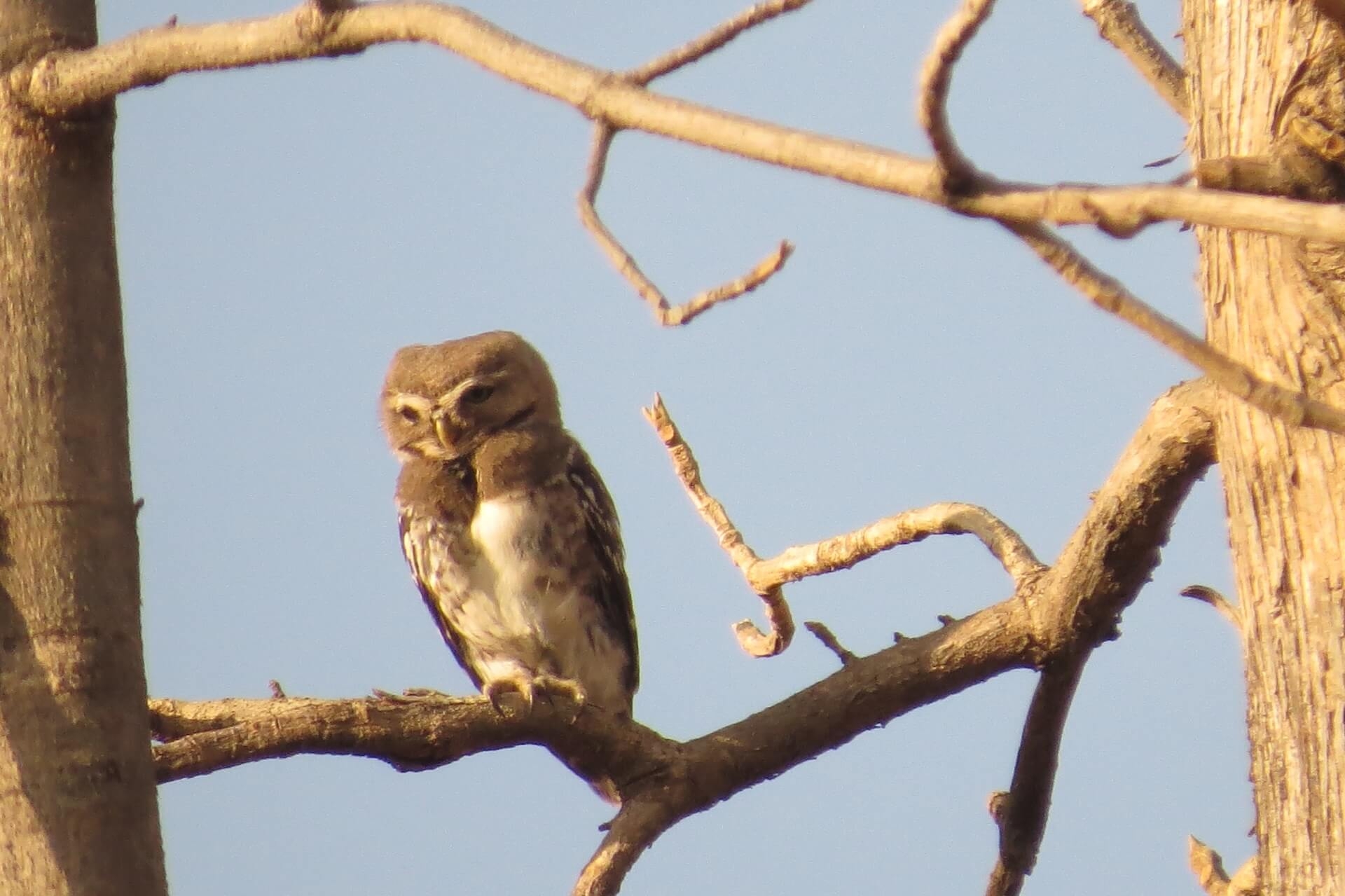
The Forest Owlet, an endangered species native to Central India's dry deciduous forests, faces threats from habitat loss and degradation. Conservation efforts in Madhya Pradesh aim to protect its habitat, estimate its population, and involve local communities through sustainable climate friendly practices, such as improved cook stoves.



- (iv) Environmental Sustainability
- (iii) Promoting Gender Equality
- (x) Rural development
Madhya Pradesh
Open for funding
Existing Project
Executive Summary
The Forest Owlet (Athene blewitti) is an endangered diurnal owl species endemic to Central India, predominantly found in teak-bearing dry deciduous forests. It prefers plains over hilly regions and high elevations. The owlet's population is dispersed and currently documented in 12 locations across Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat. Despite its presence in these areas, there is no comprehensive population estimate. The Forest Owlet is an obligate cavity-nester, making the preservation of cavity-bearing trees essential for its breeding. The main threats to its survival include deforestation due to encroachment, and forest degradation from tree cutting, forest fires, and grazing. Production forestry, particularly in the Khandwa and Burhanpur districts, significantly alters the forest structure, further threatening the owlet's habitat.
Owls, including the Forest Owlet, play a crucial ecological role by feeding on rodents. A single owl can consume up to 1,000 mice annually, preventing significant crop damage. The Forest Owlet, an iconic species, survives in isolated populations and requires forested habitats for roosting, cavity-bearing trees for nesting, and forest edges for foraging. Without these resources, the owlet will face local extinction. Owls are specialized raptors, crucial for maintaining ecological balance by preying on agricultural pests like rodents and insects. A recent report on India's bird populations highlighted a rapid decline in raptors, including owls, which poses a severe ecological threat. As apex predators, a decline in raptor populations can lead to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
A comprehensive conservation project is being implemented for conservation of the Forest Owlet in the Khandwa and Burhanpur districts of Madhya Pradesh. The project aims to accurately estimate the Forest Owlet's population to better understand its endangered status. Collaboration with the Madhya Pradesh Forest Department will facilitate the development of forestry practices conducive to the owl's conservation. Additionally, nest boxes will be installed to provide alternative nesting sites. Engaging local communities intensively, the project will co-develop solutions like firewood woodlots to mitigate threats to the Forest Owlet and support its conservation. Improved cook stoves (ICS) will be introduced in project villages to reduce firewood consumption, thus alleviating the pressure on forest resources and preserving the owlet's habitat.
The proposed project builds on previous work in the area and will implement actions to protect the Forest Owlet's habitat in Reserved Forests. The project aims to establish a large, continuous population spanning Melghat, Burhanpur, and Khandwa. The project area is strategically located within the tiger corridor between the Satpura Tiger Reserve and the Melghat Tiger Reserve. Strengthening this corridor is a crucial intervention of the project, ensuring the Forest Owlet's conservation and enhancing the overall ecological health of the region.
About the NGO
Wildlife Research and Conservation Society (WRCS) was established in 2005 for conserving wildlife and biodiversity of the country based on scientific principles and scientific information. We carry out research studies on endangered species and important conservation issues. We implement projects in partnership with the Forest Department and the local community. At all project sites we carry out livelihood activities for the community. At present our main areas of work are (a) conservation of private forests, (b) sustainable tiger habitat conservation, (c) ecological study of forest owlet and (d) mitigation of human elephant conflict in partnership with the community.
Please Login to view the additional details or Register as Donor
- Problem Statement
- Larger Context
- Proposed Intervention
- Geography and demography
- Methodologies and activities
- Budget
- Additional Details